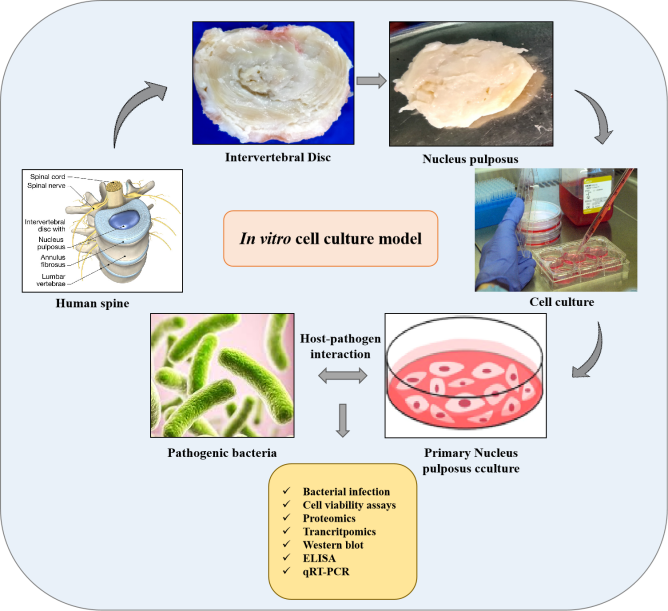
Validation of subclinical infective etiology mediated disc degeneration
Intervertebral disc degeneration causing low back pain is the frequent disease and individual at any age may suffer with this disease. IVD is composed of three main components including nucleus pulposus (NP), annulus fibrosus (AF) and cartilage end plate (CEP). Disc degeneration is caused by various factors and GOREF hypothesize subclinical infection mediated disc degeneration based on the research carried out in proteomics and metagenomics. Our metagenomics study revealed the identification of several pathogenic bacteria from degenerated discs. The cell culture intends to study the interaction of the pathogenic bacteria with the cultured primary nucleus pulposus cells. The interaction and the pathogenic virulence would be assessed by checking cell viability, expression of ECM markers, inflammatory markers and apoptotic markers as well by OMICS approach after infection.
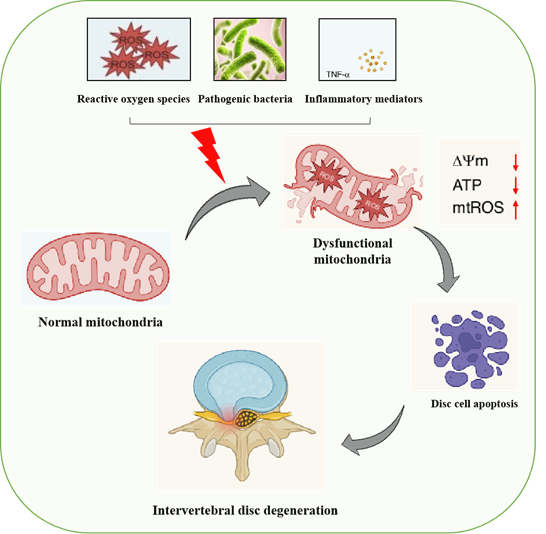
Role of mitochondrial dysfunction during disc degeneration
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles and are the centre hub for cellular energy. Its function includes reactive oxygen species production, metabolism, and energy production, cellular apoptosis, and mitophagy, which makes them an important organelle for normal physiological functions. Mitochondrial dysfunction are associated with various pathological conditions, including IVDD. Oxidative stress, inflammatory mediators, and subclinical infection, during IVDD, cause mitochondrial dysfunction. This leads to imbalance mitochondrial dynamics and impaired mitophagy, results in the accumulation of damaged mitochondria inside the disc cell and causing apoptotic death of disc cells. Using in vitro model systems, the effect of ROS, inflammatory mediators, and bacterial pathogens in nucleus pulposus primary cultures and degenerated tissues will be assessed to understand the pathogenesis of IVDD mediated by mitochondrial dysfunction.